What is Asset Tracking? Learn How It Works, Why Its Important, Its Purpose, Benefits and How to Track Assets


Asset tracking is a crucial aspect of any business operation, especially for companies that rely on physical assets to carry out their day-to-day activities. Whether it’s equipment, vehicles, or inventory, knowing the location and status of your assets at all times is essential for efficiency, cost-saving, and security.
Asset tracking is the process of monitoring and managing assets throughout their lifecycle. By using technology such as GPS, RFID tags, or barcode scanners, businesses can track the movement, usage, and maintenance of their assets in real time. This not only helps in preventing loss or theft but also ensures that assets are utilized optimally and are in good working condition.
In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at asset tracking, market trends, asset tracking technologies, and software. We’ll also discuss common asset tracking challenges and benefits and describe how to implement an effective asset tracking system.

Asset tracking refers to the process of monitoring and managing physical assets throughout their lifecycle. This includes tracking the location, status, and usage of assets such as equipment, vehicles, tools, and inventory. By using technologies like RFID, GPS, and barcode scanners, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce theft and loss, and optimize asset performance and utilization.
Asset tracking also helps organizations with compliance, maintenance schedules, and overall cost control. It’s essential for businesses looking to optimize their operations and maximize their return on investment.
Asset tracking is used across many industries for various applications, such as:

The terms ‘asset tracking’ and ‘inventory tracking’ are sometimes used interchangeably, and while they may seem similar, there are important differences between the two.
Asset tracking involves managing and monitoring physical assets such as equipment, machinery, vehicles, or technology devices. The goal of asset tracking is to maintain detailed documentation about a company’s assets, including their location, condition, and maintenance history.
Inventory tracking, on the other hand, focuses on monitoring the goods that a business buys, sells, or uses in its operations. This includes raw materials, finished products, and supplies. Inventory tracking helps businesses to keep accurate records of their stock levels, reorder products when necessary, and prevent stockouts or overstocks.
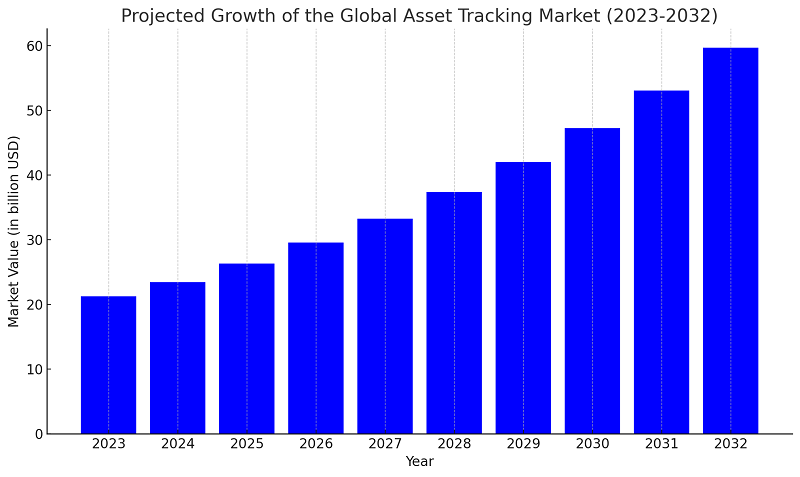
The asset tracking market includes asset tracking hardware such as RFID, GPS, and barcode technologies, as well as the on-premise and cloud-based asset tracking software that supports them. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global asset tracking market size was valued at an estimated $21.25 billion in 2023. It’s expected to grow at a 12.4% CAGR, growing from $23.42 billion in 2024 to $59.64 billion by 2032.
There are multiple factors driving growth in the asset tracking market, including:
| Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| RFID |
|
|
| Barcode Labels & Asset Tags |
|
|
| GPS |
|
|
| IoT |
|
|
| QR codes |
|
|
| Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) |
|
|
| Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) |
|
|
Asset tracking technologies include hardware and software. Hardware includes technologies such as barcode labels, RFID, GPS, and IoT devices.
Asset tracking software solutions (both on-premise and cloud-based) integrate with asset tracking hardware, enabling businesses to maintain a central asset database, streamline documentation and reporting to drive decision-making, and monitor and manage their assets in real time.
Let’s take a look at the different types of asset tracking technologies.

RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that allows for the identification and tracking of assets using radio waves. RFID tags are small, electronic devices that consist of a microchip and an antenna. These tags can be attached to assets such as equipment, tools, inventory, or vehicles, allowing them to be easily scanned and tracked.
RFID technology has revolutionized asset tracking by providing real-time visibility into the location and status of assets. Unlike traditional barcode systems, RFID does not require line-of-sight to read tags, making it faster and more efficient for tracking assets in a variety of environments.
RFID for asset tracking offers numerous benefits for businesses, including:
However, there are also some downsides to using RFID for asset tracking. Keep these considerations in mind when selecting asset tracking technologies:

Barcode labels are unique identifiers that are attached to assets, such as equipment, inventory, or furniture. These labels contain a series of black and white bars that can be scanned with a barcode scanner to quickly retrieve information about the asset.
Asset tags are durable labels—often containing barcodes—that are designed to withstand harsh environments and prolonged use. They are typically made of materials like polyester, metal, or tamper-evident materials to ensure longevity.
According to Gitnux, 47% of organizations use barcodes for asset tracking. Asset tracking using barcode labels and asset tags is a cost-effective and efficient way to monitor and manage your assets.
With a barcode scanner, you can easily scan the barcode labels on your assets to keep track of their location, maintenance history, and depreciation schedule. This real-time data allows you to make informed decisions about asset allocation, reordering, and maintenance scheduling.
When choosing barcode labels and asset tags for asset tracking, it’s important to consider the durability, readability, and ease of scanning. High-quality labels and tags should be able to withstand harsh conditions like extreme temperatures, moisture, and abrasion. Additionally, the barcode should be printed clearly and accurately to ensure smooth scanning without errors.
For example, Camcode’s Foil Metalphoto® Labels and Rigid Metalphoto® Labels are made of Metalphoto®, the most durable printed aluminum substrate available. In fact, Metalphoto photosensitive anodized aluminum has been trusted for more than 50 years by the U.S. Armed Forces, NASA, Boeing, and Caterpillar. In a study conducted by the U.S. Navy, Camcode’s Metalphoto photosensitive anodized aluminum labels earned more high scores than any other label material evaluated.
Metalphoto’s durability is thanks to a unique manufacturing process in which a silver halide image is sealed beneath a sapphire-hard, anodic layer of aluminum. Barcode labels and asset tags made of Metalphoto offer exceptional durability, maintaining their original appearance and scanning performance even after exposure to UV, harsh weather, salt spray, chemicals and abrasion, industrial solvents, and chemicals. These labels have an expected exterior lifespan of more than 20 years.
Teflon™ Coated Metalphoto® Barcode Labels are another durable option, featuring a non-stick Teflon fluorocarbon film coating that sheds paint, acids, strong caustics, and chemicals, making them ideal for harsh environments. For applications in which assets are exposed to high temperatures, Extra High Temperature Labels can withstand temperatures of up to 1200 degrees Fahrenheit.
Not all asset tracking applications require this level of durability. For these less-demanding applications, Premium Polyester Plus Labels with Heavy Adhesion Strength are an excellent choice. These labels are particularly well-suited for industrial applications that require heavy adhesion strength, and they offer an expected exterior lifespan of up to two years.
Tamper-Evident Polyester Labels are ideal for tagging assets that are prone to theft, tampering, or unauthorized transfer. When the label is removed, a “VOID” message is revealed on both the label material and the mating surface, providing evidence of tampering. These labels offer good resistance to general purpose and household cleaners, mild acids, oil, and water, with an exterior lifespan of up to two years.
Camcode also offers a large selection of asset tags and barcode labels designed for specific applications. For example, Camcode’s UID labels meet the requirements of MIL-STD-130 and MIL-STD-129. We also offer utility maintenance tracking labels, such as Bar Code Tags for Utility Pole Applications, manufacturing asset tag solutions, such as Removable Paint Mask Bar Code Labels for One-Time Painting Line, and much more.
With decades of experience in automatic identification and data capture, Camcode’s experts can help you select the best asset tracking solution for your application’s needs. Get in touch with Camcode today to learn more.

GPS (Global Positioning System) for asset tracking refers to the use of satellite-based navigation technology to monitor and manage the location and movement of assets in real-time. It plays a vital role in asset tracking by providing accurate location data that can be accessed through web-based platforms or mobile applications.
GPS is used across multiple industries, such as:
There are several key benefits of using GPS for asset tracking:

The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the network of physical objects or “things” that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable these objects to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. These objects can range from everyday household items like smart thermostats and kitchen appliances to industrial equipment in factories and even vehicles.
With the help of IoT (Internet of Things) technology, companies can now track assets in real-time, gain valuable insights, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their operations.
One of the key advantages of using IoT for asset tracking is the ability to collect and analyze data from sensors attached to assets. These sensors can monitor various parameters, such as location, temperature, humidity, and movement, to provide real-time visibility into the status of assets. This data can then be transmitted to a central system for analysis and visualization, allowing managers to track assets remotely and identify potential issues before they escalate.
IoT-enabled asset tracking systems can automate inventory management processes, minimize manual errors, and improve overall efficiency. For example, sensors installed in warehouses can monitor inventory levels, track the movement of goods, and send alerts when stock levels are running low. This real-time visibility can help companies reduce stockouts, prevent overstocking, and streamline their supply chain operations.
In the transportation and logistics industry, IoT technology has enabled companies to track vehicles, monitor driver behavior, and optimize routes for better efficiency. By equipping vehicles with GPS trackers and sensors, companies can collect data on location, fuel consumption, driving patterns, and maintenance needs. This data can then be used to improve fleet management, reduce fuel costs, and enhance driver safety.
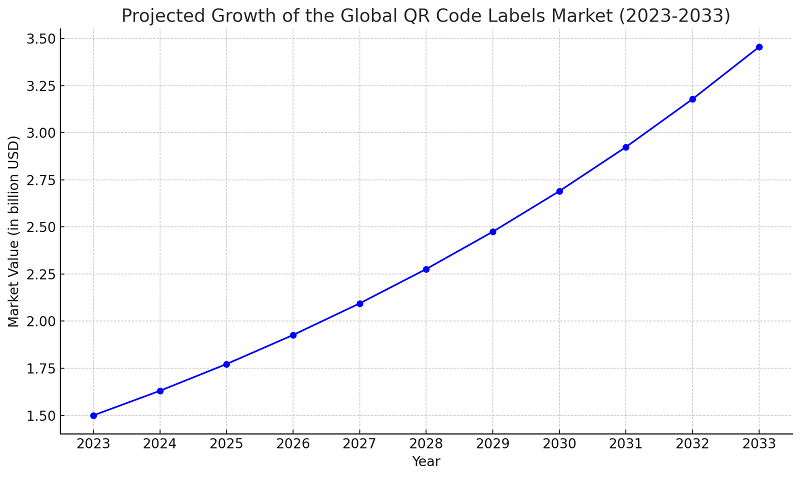
QR codes for asset tracking have become an increasingly popular and efficient way for businesses to keep track of their inventory, equipment, and other valuable assets. QR codes, which are two-dimensional barcodes that can be scanned with a smartphone or other mobile device, are a cost-effective solution for tracking assets in real-time.
According to Future Market Insights, the global QR code labels market was valued at an estimated $1.5 billion in 2023. With growth projected at an 8.7% CAGR from 2023 to 2033, it’s projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2033.
One of the main advantages of using QR codes for asset tracking is the ease of use. With a simple scan of the QR code tag, all relevant information about the asset can be accessed instantly. This can include details such as the asset’s location, maintenance history, warranty information, and more. This makes it easy for employees to quickly identify and locate assets when needed.
In addition to ease of use, QR codes also offer a high level of accuracy in asset tracking. By scanning the QR code, employees can update information in real-time, ensuring that the asset’s location and status are always up to date. This reduces the risk of human error and helps prevent the loss or misplacement of valuable assets.
QR codes can also help improve overall efficiency and productivity in the workplace. With assets being easily accessible and trackable, employees can spend less time searching for equipment or inventory and more time focusing on their tasks. This can lead to increased productivity and cost savings for businesses.

Bluetooth Low Energy, also known as Bluetooth Smart, is a wireless personal area network technology that is designed to provide significantly lower power consumption compared to classic Bluetooth. It was introduced as part of the Bluetooth 4.0 specification in 2010 and has since become a popular choice for a wide range of devices and applications.
One of the key features of Bluetooth Low Energy is its ability to operate in a connectionless mode, where devices can broadcast data without the need for a constant connection. This makes it ideal for applications such as beacon technology, where devices can broadcast their presence to nearby devices without the need for complex pairing processes.
Asset tracking using BLE technology involves attaching small, battery-powered beacons to assets that need to be monitored. These beacons emit a BLE signal that can be picked up by BLE-enabled devices, such as smartphones or IoT sensors. By using an app or software platform, users can view the real-time location of their assets, as well as receive alerts and notifications if an asset moves out of a designated area.
One of the key advantages of using BLE for asset tracking is its low power consumption. BLE beacons can operate for months or even years on a single coin cell battery, making them ideal for long-term tracking applications. Additionally, BLE technology offers precise location tracking, with the ability to pinpoint assets within a few meters of their actual location.
Another benefit of BLE asset tracking is its scalability. BLE beacons can be easily deployed in large facilities or outdoor environments, providing comprehensive coverage and accurate asset monitoring. This scalability makes BLE technology suitable for a wide range of industries, including logistics, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
Bluetooth Low Energy also offers improved security features, including encryption and authentication, to ensure that data exchanged between devices is secure and protected from unauthorized access.
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) are advanced technology solutions designed to automatically identify and track the location of objects in real time, often within a confined area or facility.
RTLS uses a combination of technologies such as GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and sensors to track the location of assets in real-time. Tags are attached to assets, allowing them to be monitored and tracked throughout the facility or even across multiple locations. The signals they generate are read by readers or sensors, which are strategically placed throughout the coverage area or facility.
The data from the tags and readers is captured, processed, and displayed on a centralized dashboard or software platform for analysis. This interface provides real-time maps, reports, and alerts, allowing users to monitor and manage assets effectively.
RTLS can be scaled to track a wide range of assets across different locations and environments. This flexibility makes it suitable for various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and retail.
However, the cost of deploying an RTLS is high, involving expenses for hardware (tags, readers, sensors), software, and infrastructure setup. Ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and equipment replacement add to the total lifetime cost.
Additionally, installation is complex. Proper installation and configuration requires technical expertise, and it may require modifications to existing infrastructure, such as adding new power sources, network cabling, or structural changes to accommodate readers and sensors.
Physical obstacles like walls, furniture, and machinery can interfere with signal transmission, affecting the accuracy of the system. Other wireless devices and electronic equipment can also cause interference, reducing the reliability and precision of location data.
Asset tracking software works by using barcodes, RFID tags, or GPS to assign unique identifiers to each asset. These identifiers are then scanned or read by a mobile device or scanner, which records the asset’s location, status, and other relevant information in a centralized database. This database can be accessed in real-time by authorized users, allowing them to track the movement and condition of assets throughout their lifecycle.
Asset tracking software helps businesses prevent loss and theft by providing real-time visibility into the location of assets. This can also help companies optimize asset usage and maintenance schedules, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency. Additionally, asset tracking software can help businesses comply with regulations and standards related to asset management, such as ISO 55000.
When choosing asset tracking software, businesses should consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, integration with other systems, and reporting capabilities.

Good asset management is crucial for the productivity and success of any organization. Poor asset management can result in significant costs related to productivity loss, inefficiencies, and missed opportunities. Here’s a look at the risks associated with poor asset management practices.
One of the most obvious productivity costs of poor asset management is downtime and equipment failure. When assets are not properly maintained or monitored, they are more likely to break down unexpectedly, leading to unplanned downtime.
Downtime can have a significant impact on productivity, as it means that employees are unable to perform their tasks and production is halted. This can result in missed deadlines, lost revenue, and a negative impact on customer satisfaction.
Poor asset management can also lead to poor asset utilization. This means that assets are not being used to their full potential, resulting in wasted resources and inefficiencies.
For example, if an organization has excess inventory sitting in a warehouse, it is tying up capital that could be used more effectively elsewhere. Similarly, if equipment is not being utilized to its full capacity, it is not generating the maximum return on investment for the organization.
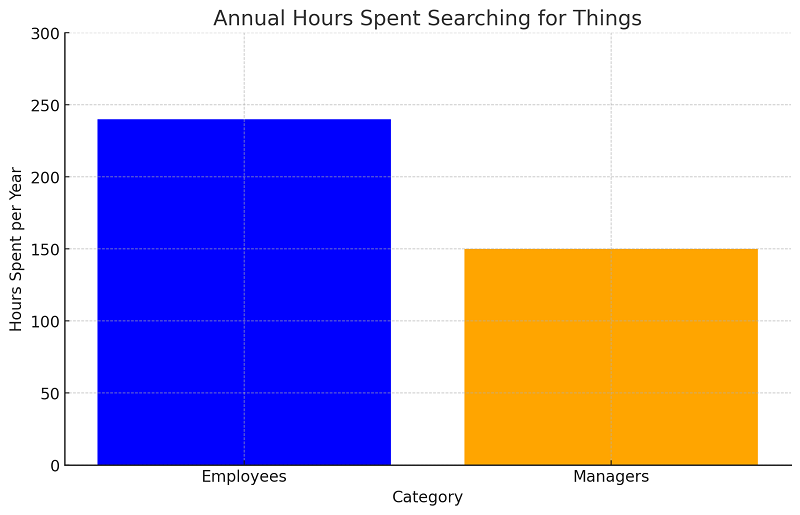
Without proper asset tracking and management tools, organizations may struggle to accurately track and monitor their assets. This can lead to issues such as misplaced assets, lost inventory, and inaccurate asset records.
Without visibility and control over assets, organizations may struggle to make informed decisions about resource allocation, asset maintenance, and replacement. This can result in wasted time and resources, as well as missed opportunities for optimization.
For example, according to A Clear Path, employees spend an average of 1.5 hours each day—or 6 weeks per year—looking for things. Managers waste an average of 150 hours each year—which equates to nearly a full month—searching for lost information. For a professional earning $100,000 per year, that equates to a loss of $7,684 annually.
Poor asset management can also expose organizations to compliance and regulatory risks. For example, if assets are not properly tracked and maintained, organizations may fail to meet regulatory requirements for asset safety and maintenance. This can result in fines, legal penalties, and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Compliance and regulatory risks can also result in disruptions to operations, as organizations may be forced to cease operations until they are able to demonstrate compliance with regulations.
| Industry | Uses/Benefits |
|---|---|
| Logistics & Supply Chain Management |
|
| Construction |
|
| Healthcare |
|
| Manufacturing |
|
| Retail |
|
| Education |
|
| Transportation & Logistics |
|
| Government & Defense |
|
Asset tracking is a valuable tool that can be utilized in a wide range of industries to improve efficiency, increase visibility, and reduce losses. Here are some industries that commonly use asset tracking systems:
Asset tracking is essential in the logistics and supply chain industry to monitor the movement of goods and ensure they reach their destination in a timely manner. By tracking assets such as containers, vehicles, and packages, companies can optimize their operations, reduce delays, and improve customer satisfaction.
Construction companies often deal with high-value equipment and tools that are constantly moving between job sites. Asset tracking systems help construction managers keep track of their assets, prevent theft, and ensure that the right equipment is available when needed.
Hospitals and healthcare facilities use asset tracking to manage medical equipment, devices, and supplies. By tracking assets in real-time, healthcare providers can improve patient care, reduce equipment downtime, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing is the largest end-user industry for asset tracking. It’s vital for monitoring the location and status of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. By implementing asset tracking systems, manufacturers can optimize their production processes, prevent inventory shortages, and reduce costs.
Retailers use asset tracking to manage inventory, track merchandise shipments, and prevent loss from theft or misplacement. By tracking assets throughout the supply chain and in-store locations, retailers can improve stock management, reduce out-of-stock situations, and enhance the shopping experience for customers.
Educational institutions use asset tracking to manage school assets such as laptops, tablets, and classroom equipment. By tracking these assets, schools can prevent loss, improve asset utilization, and ensure that students have access to the necessary resources for learning.
Asset tracking is essential for the transportation and logistics industry as it helps companies monitor the location of vehicles and cargo in real-time, optimize operations, reduce theft and loss, streamline route planning, and improve fuel consumption. By using asset tracking labels, companies can also monitor maintenance schedules, reduce downtime, and minimize costly repairs, ultimately maximizing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction.
Government and defense agencies use asset tracking technologies like GPS, RFID, and UID to monitor and manage equipment, vehicles, and resources in real-time to ensure operational efficiency, security, and effective service delivery to the public. The use of asset tracking also helps prevent loss or theft of sensitive equipment and unauthorized access.

Managing physical assets such as equipment presents several challenges across various dimensions. Here are some key challenges:
Asset management involves bringing together various systems, processes, and data in order to effectively monitor and maintain assets. Different assets may use different technologies and require different maintenance practices, which can make it difficult to integrate everything seamlessly.
Additionally, as assets age and technology evolves, the complexity of integrating new systems and data sources only increases. This can result in inconsistencies, data silos, and inefficiencies, making it harder to make informed decisions about asset performance and maintenance.
The increasing complexity and interconnectedness of digital systems poses data security risks in asset management. With the use of IoT devices, RFID, and cloud-based platforms, there are more entry points for cyber attacks to compromise sensitive data.
The sheer volume of data generated by physical assets can be overwhelming, making it difficult to properly secure and monitor all information. The constant evolution of cyber threats means that security measures must be continuously updated and improved to keep up with potential vulnerabilities.
A lack of standardization in asset management can lead to inconsistencies in data collection, reporting, and decision-making. Without standardized processes and procedures, it becomes difficult to track and monitor assets accurately, which can result in inefficiencies, errors, and potential financial losses.
A lack of standardization also can make it challenging to compare asset performance, maintenance practices, and operational costs across different facilities or organizations. This ultimately hinders the ability to optimize asset utilization, streamline maintenance processes, and make informed strategic decisions.
Upfront costs can include purchasing equipment, machinery, or technology, as well as hiring and training staff to operate and maintain these assets. This financial burden can put a strain on a company’s cash flow and profitability, especially if the assets do not generate revenue right away.
Some asset management components have a higher upfront cost than others. RFID, for example, is costlier to implement compared to asset tags and barcode labels.
Developing an asset management system often involves implementing new processes and technologies that users are unfamiliar with. Employees are often resistant to change and may be hesitant to learn new systems or procedures.
User onboarding and training can be time-consuming and costly, especially if it requires bringing in external consultants or investing in specialized software. Without proper training and user adoption, companies may experience inefficiencies and missed opportunities for optimization.
The sheer volume and complexity of assets involved make it challenging to maintain accurate data and documentation. With various assets spread across multiple locations and departments, keeping track of all the data and documentation can be incredibly time-consuming and prone to human error.
Additionally, physical assets are constantly being used, moved, and modified, making it difficult to ensure that all information is up to date. Without accurate data and documentation, it becomes challenging to make informed decisions about asset maintenance, repairs, and replacements, ultimately leading to inefficiencies and higher costs in the long run.

An effective asset tracking system is the key to overcoming the asset management challenges described above. Here’s a more detailed look at the benefits of implementing a comprehensive asset tracking and management system.
Effective asset tracking improves asset visibility by providing real-time information on each asset’s location, condition, and status. By knowing exactly where assets are at all times, companies can optimize their use, prevent loss or theft, and schedule maintenance more efficiently.
Increased visibility into the location and status of each asset also allows businesses to optimize the allocation of resources, minimize downtime, and reduce the risk of lost or stolen assets. By knowing the precise location of assets at all times, companies can prevent over-utilization or under-utilization of resources, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
Additionally, asset tracking systems can provide valuable data on asset usage patterns, helping businesses make informed decisions about resource allocation and future investments.
Effective asset tracking helps maintenance teams stay proactive by scheduling regular maintenance tasks based on actual usage and wear and tear data. With accurate asset tracking, maintenance managers can identify potential issues before they become major problems, reducing downtime and increasing asset lifespan.
Asset tracking also allows for better inventory management, ensuring that spare parts and tools are readily available when needed, further streamlining maintenance processes.
Asset theft and loss can lead to significant financial losses and operational disruptions. Asset tracking technologies like GPS tracking, RFID tags, and IoT sensors can alert companies to unauthorized movements or access, enhancing security and reducing the likelihood of theft and loss.
Businesses continuously seek ways to cut costs and enhance their bottom line. Asset tracking systems minimize expenses by preventing asset misplacement, reducing theft, optimizing maintenance schedules, and minimizing downtime due to equipment failures, which directly impact profitability.
According to Tech Talk, a survey of 558 businesses using computerized maintenance management software (CMMS) found that 20.1% of respondents realized a reduction in equipment downtime and 19.4% reported savings in material costs. Additionally, manual labor costs are reduced as employees spend less time searching for misplaced items or information.
Because asset tracking supports more effective maintenance management, companies can ensure assets are in optimal working condition. This can improve an asset’s performance and extend its useful lifespan.
Effective asset tracking supports data-driven decision-making by providing real-time and accurate information on the location, condition, and usage of assets. This data allows businesses to optimize asset utilization, identify trends and patterns, and make informed decisions about maintenance and replacement.
This data-driven approach helps businesses make strategic decisions that can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and improved performance overall.
Asset tracking ensures that all assets are properly accounted for, tracked, and maintained. By having a clear understanding of what assets a company owns and how they are being utilized, organizations can easily provide accurate information to regulators and stakeholders.
Additionally, effective asset management can help identify any potential risks or issues related to compliance, allowing companies to address them proactively and maintain a strong level of compliance. This, in turn, helps to build trust with investors and customers, as it demonstrates transparency, responsibility, and good governance practices.
Effective asset tracking can help companies better manage risks. Visibility into every asset’s location and status reduces the risk of loss or theft.
Tracking assets can also help prevent breakdowns or equipment failures, reducing the risk of costly downtime. With accurate and up-to-date information on asset usage and maintenance schedules, companies can better plan for potential risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
Effective asset tracking systems enable businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing overstock and stockouts. It also facilitates the efficient tracking of equipment usage and maintenance, ensuring that assets are in good working condition and readily available when needed.
This leads to smoother operations and can significantly enhance productivity. According to IBM, 28% of companies using a CMMS or similar solution saw improved maintenance productivity.
The ability to quickly scan a barcode to identify assets and access valuable information such as the manufacturer, spare parts suppliers, maintenance history, and operations and maintenance procedures saves significant time employees might otherwise spend searching for information.
A robust asset tracking and management system enables employees to quickly identify assets and document maintenance tasks and other information, reducing the human error common in manual documentation procedures. For example, in one study, implementing bar-code medication administration (BCMA) technology reduced medication administration errors by 43.5% and resulted in a 55.4% decrease in actual patient harm events.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Barcode/RFID Integration | Offers barcode or RFID integration to easily scan and track assets in a fast and efficient manner, eliminating manual data entry, reducing human error, and saving time. |
| Real-time Tracking | Provides real-time tracking capabilities to monitor the location and status of assets at any given time, crucial for businesses with frequently moving or widely spread assets. |
| Lifecycle Management | Tracks the entire lifecycle of assets, from acquisition to disposal. |
| Customizable Reporting | Offers customizable reporting options to analyze asset data and generate insightful reports, allowing tracking of maintenance schedules, depreciation, and overall asset performance. |
| Mobile Compatibility | Allows tracking of assets on-the-go using a smartphone or tablet, providing flexibility and convenience, especially for businesses with field employees or remote workers. |
| Alerts and Notifications | Offers alerts and notifications for important asset-related events, such as maintenance due dates or asset movement, ensuring timely actions and preventing asset loss or damage. |
| Integration with Other Systems | Integrates seamlessly with other systems, such as inventory management or accounting software, ensuring data synchronization for consistency and accuracy, and streamlining processes across departments. |
| Analytics | Provides comprehensive analytics capabilities, offering insights into asset utilization, maintenance needs, and performance. |
| Scalability | Scalable to accommodate growing asset tracking needs, ensuring the software can expand with the business and adapt to future requirements. |
Asset tracking software is a key component for effective asset and inventory management. With so many options available in the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right software for your specific needs. To help you make an informed decision, here are some key features and capabilities to look for in asset tracking software:

Follow these steps and best practices to successfully implement an asset tracking system.

Implementing an asset tracking system from scratch can be overwhelming. In addition to durable asset labels for a variety of applications, Camcode also offers asset management services to help you implement an asset tracking system effectively, such as on-site consultation and project management to help you determine your goals, establish a timeline for implementation, and evaluate potential risks and policy requirements. Camcode also assists with implementation and project planning to ensure your success.
Camcode also offers data reconciliation and asset inventory. We’ll help you match your data to your inventory items and cleanse your existing databases and inventory records to eliminate inaccuracies and discrepancies. In addition, Camcode offers data management, label installation, project reporting, and other customized services to ensure successful implementation and management. Contact us today to learn more or request a quote.
Assets are long-term resources owned by a company that are used in the operation of the business and provide future economic benefits. These include equipment, vehicles, buildings, and technology.
Inventory, on the other hand, consists of goods or materials that a business holds for the purpose of resale or production. While assets are typically used over a long period, inventory is often sold or consumed within a short cycle.
The three primary goals of asset management are:
The best way to identify assets is by using a combination of unique identifiers such as barcodes, RFID tags, or serial numbers. These identifiers should be linked to detailed records in an asset management system, capturing essential information such as asset type, location, purchase date, and maintenance history.
Consistent and standardized identification practices help in accurately tracking and managing assets throughout their lifecycle.
To conduct an asset inventory, start by planning the inventory process, including defining the scope and setting objectives. Create a comprehensive list of all assets to be inventoried. Use tracking technologies like barcodes or RFID tags to label each asset.
Conduct a physical count of all assets, recording their details in an asset management system. Verify and reconcile the recorded data with existing records, and address any discrepancies. Regularly update and maintain the inventory to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Industrial asset tracking is the process of monitoring and managing the location, status, and usage of physical assets—such as machinery, equipment, vehicles, and tools—within an industrial environment using technologies like barcodes, RFID, GPS, or IoT sensors. This practice provides real-time or periodic visibility into where assets are, how they are being used, and their condition, which helps enhance operational efficiency, reduce losses, and improve maintenance and resource allocation
An asset life cycle refers to the stages an asset goes through from acquisition to disposal. These stages typically include planning and procurement, installation and commissioning, operation and maintenance, and finally, decommissioning and disposal. Managing the asset lifecycle effectively ensures optimal performance, prolongs the asset’s useful life, and maximizes return on investment.
Our sales engineers are experts in automatic asset tracking, tagging and identification,a nd can answer all your questions. Get in touch now.
Lets Talk ›Enter your information and get a free checklist of the top questions to answer and tips to plan a successful asset tagging project for any asset management or tracking system implementation.