What is RFID? How Does It Work?
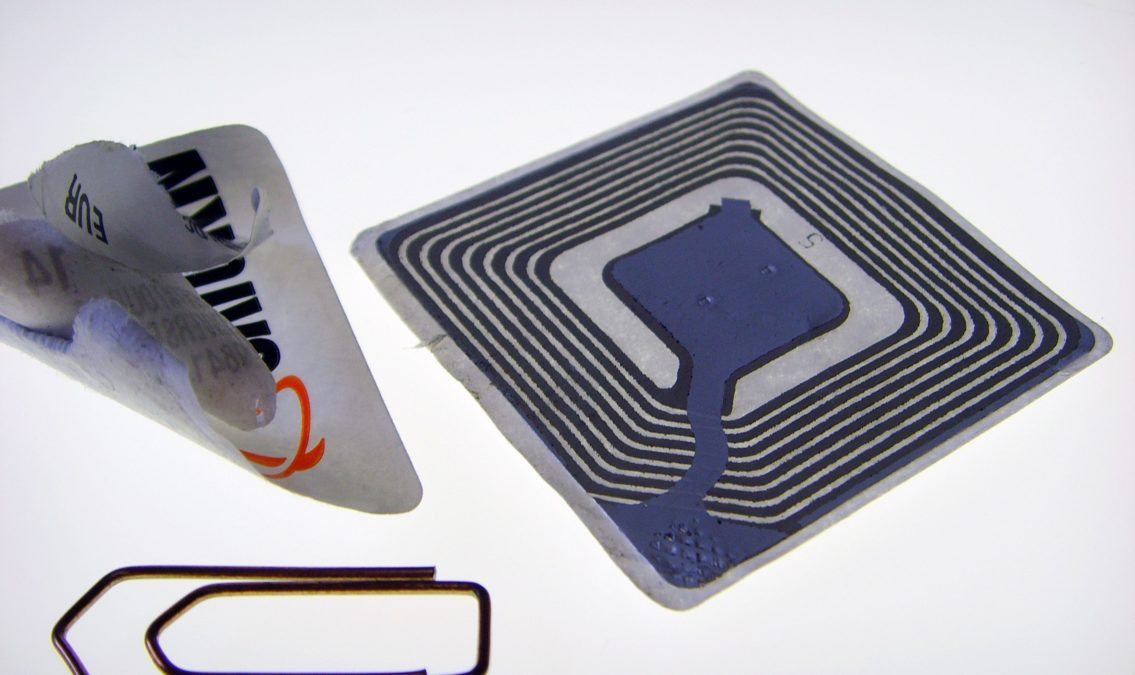

Radio frequency identification (RFID) is in everything from amusement park passes to payment solutions. This wireless technology allows businesses to automatically identify and track objects, tools, equipment, vehicles, and more.
In recent years, RFID technology has become increasingly popular and has found numerous applications in various industries, including retail, logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing. But how does RFID work, and how can businesses leverage it?
Check out this guide to learn what RFID is, how it works, how it differs from other tagging technologies, and the potential benefits of RFID.

RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to transmit data from an RFID tag to a reader that logs the data. The system consists of three main components: an RFID tag, an RFID reader, and a computer system.
A business places an RFID tag on or inside an object, such as a retail product or a piece of industrial machinery. The tag contains a microchip that stores data, as well as an antenna that receives and transmits radio signals.
When an RFID reader emits a radio frequency signal, the tag detects it and responds with the data stored in its memory. The reader then captures the data and sends it to a computer system for processing.
RFID systems can use different frequencies (Low-frequency, High-frequency and Ultra-high frequency) which we’ll discuss in greater detail below.
RFID tags can be either passive or active. Passive RFID tags don’t have a built-in power source and rely on energy provided by an RFID reader. Active RFID tags, on the other hand, have a built-in po
There are two types of RFID tags: passive RFID tags and active RFID tags (also known as battery-powered RFID tags).
There are three different types of RFID systems, which vary by the frequency band within which they operate: low frequency, high frequency, and ultra-high frequency. The frequency simply means the size of the radio waves used to communicate between the RFID tags and readers.
Because the radio waves behave differently at each frequency, there are pros and cons of using each.

Whether you’re a retailer, a healthcare provider, or a manufacturer, you likely use a mix of different tagging solutions throughout your organization. Barcodes and QR codes are some of the most common options for businesses, but RFID works differently.
Barcodes are a visual tagging technology that uses a series of bars and spaces to represent data. Barcodes are inexpensive and easy to produce, but they require a direct line of sight to a reader and have a limited storage capacity.
In contrast, you can read RFID tags from a distance. They also have a much larger storage capacity than barcodes.
QR codes are a two-dimensional visual tagging technology that uses a matrix of dots to represent data. QR codes can store more data than barcodes and can be read using a smartphone camera, but they still require a direct line of sight and aren’t as versatile as RFID tags.
RFID technology has been widely adopted for asset tracking in various industries, including retail, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. For example, retailers use RFID tags to track inventory and prevent theft, healthcare providers use RFID wristbands to track patients and medication, logistics companies use RFID to track shipments and optimize supply chain operations, and manufacturers use RFID to track products throughout the production process.
If you’re trying to embrace digital transformation in your business, RFID tags make it much easier to transmit information automatically. RFID technology has numerous benefits, including:
However, keep in mind that durable barcode labels are often a better choice for certain applications. For example, the U.S. military also uses RFID tags for some applications, although for military asset tracking, unique identification (UID) labels are more suitable for security, compliance, and durability requirements.
Because of the nature of RFID technology, there are several issues with it.

RFID and barcodes automate the process of collecting data about inventory and assets. However, RFID systems experience interference and are difficult to use with metals and liquids because those materials cause more interference.
Barcodes, on the other hand, are much less expensive and are not at risk of interference.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags are an ideal asset tracking system in certain applications. However, RFID does have some inherent shortcomings in functionality, durability and security. Click below to see the pros and cons of RFID, as well some alternatives that may be better suited to your particular tracking project.
Our sales engineers are experts in automatic asset tracking, tagging and identification,a nd can answer all your questions. Get in touch now.
Lets Talk ›Enter your information and get a free checklist of the top questions to answer and tips to plan a successful asset tagging project for any asset management or tracking system implementation.